
Ovarian Cyst Treatment in Gurgaon
Ovarian Cyst Treatment in Gurgaon
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Are Ovarian Cysts?
- Types of cyst
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis
- Treatment Options
- Why Choose Kalosa Gynae?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Introduction
At Kalosa Gynae, we specialize in providing comprehensive care for ovarian cysts in Gurgaon. Our expert team, led by Dr. Deepti Asthana, is dedicated to offering personalized and effective treatment options to ensure the best outcomes for our patients.
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets within or on the surface of an ovary. While many ovarian cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, some can cause symptoms and require treatment.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts can vary greatly in type and severity. Understanding the different types is essential for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. The main types include:
Functional Cysts
These are the most common type of ovarian cysts and often form during the menstrual cycle. They include:
- Follicular Cysts: Form when the follicle (a sac that contains an egg) does not release the egg and continues to grow.
- Corpus Luteum Cysts: Develop after the follicle releases the egg and then seals off, accumulating fluid inside.
Dermoid Cysts
Also known as teratomas, these cysts can contain tissue such as hair, skin, or teeth because they form from embryonic cells. They are usually benign but can become large and cause discomfort.
Endometriomas
These cysts are associated with endometriosis, a condition where the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows outside it. When this tissue attaches to the ovary, it can form cysts.
Cystadenomas
These cysts develop from ovarian tissue and can be filled with a watery or mucous-like fluid. They can grow quite large and may cause the ovary to twist (ovarian torsion).
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
A condition characterized by the presence of many small cysts on the ovaries. PCOS can lead to hormonal imbalances, irregular menstrual cycles, and fertility issues.
Hemorrhagic Cysts
Occur when a cyst bleeds internally. These cysts can cause abdominal pain and discomfort.
Pathological Cysts
These are less common and can be either benign or malignant. They include:
- Benign Cysts: Such as serous and mucinous cystadenomas.
- Malignant Cysts: Which may be indicative of ovarian cancer.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of ovarian cysts include:
- Pelvic pain
- Bloating or swelling
- Painful intercourse
- Menstrual irregularities
- Difficulty emptying the bladder
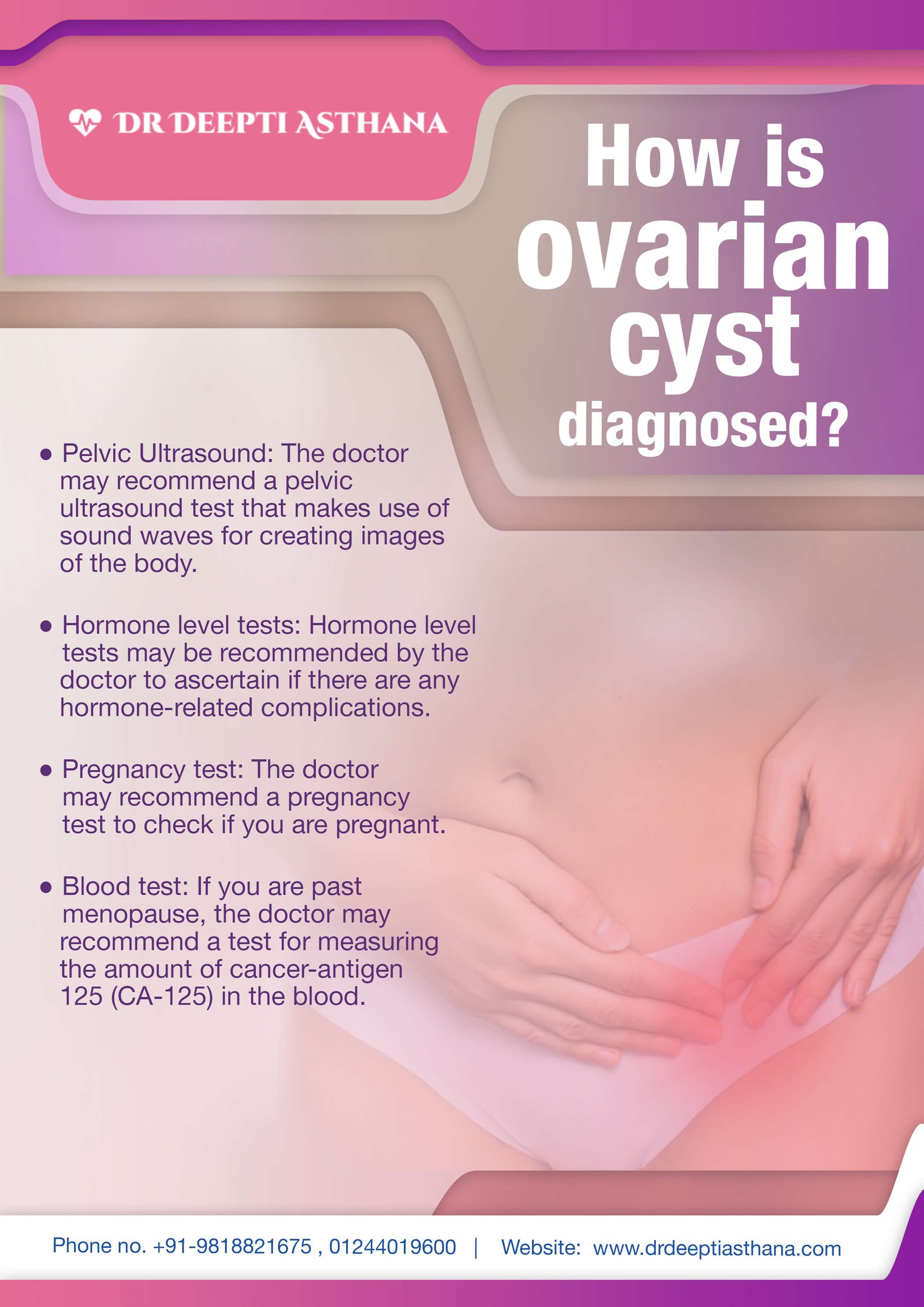
Diagnosis
Diagnosing ovarian cysts involves a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests to determine the nature, size, and potential impact of the cysts. At Kalosa Gynae, we use the following methods for accurate diagnosis:
Pelvic Examination
A pelvic exam allows the doctor to manually check for abnormalities in the ovaries or uterus. During the exam, any tenderness or unusual swelling can be an indicator of an ovarian cyst.
Ultrasound Imaging
An ultrasound is the most common and effective tool for diagnosing ovarian cysts. It uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the ovaries. There are two types of ultrasound used:
- Transabdominal Ultrasound: The probe is placed on the abdomen to get an external view of the ovaries.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: The probe is inserted into the vagina to get a more detailed image of the ovaries and the cysts.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can help determine if the cyst is causing any hormonal imbalances. Specific blood tests like CA-125 can be used to check for tumour markers that may indicate the presence of cancerous cysts, especially in postmenopausal women.
Laparoscopy
In certain cases, a laparoscopy may be performed. This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a small camera through a tiny incision in the abdomen to view the ovaries directly. It is often used if the ultrasound results are inconclusive or if there is a suspicion of endometriosis.
Treatment Options
Watchful Waiting
For many women, ovarian cysts resolve on their own without the need for treatment. If the cysts are small and asymptomatic, a watchful waiting approach may be recommended. This involves:
- Regular Monitoring: Periodic ultrasounds to monitor the size and appearance of the cyst.
- Symptom Management: Pain relievers may be prescribed to manage any discomfort.
Medications
Hormonal medications can help regulate the menstrual cycle and prevent the formation of new cysts. The types of medications include:
- Oral Contraceptives: Birth control pills can prevent ovulation and reduce the recurrence of cysts.
- Hormonal Therapy: In some cases, other hormonal therapies may be prescribed to manage underlying conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Surgery
Surgical intervention may be necessary if the cyst is large, persistent, causing severe symptoms, or suspected to be malignant. The types of surgeries offered include:
Laparoscopy
- Procedure: A minimally invasive surgery where small incisions are made in the abdomen to insert a laparoscope and surgical instruments.
- Recovery: Typically, patients can return to normal activities within 1-2 weeks.
- Advantages:Less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stay, and quicker recovery.
Laparotomy
- Procedure: A more extensive surgical procedure that involves a larger abdominal incision.
- Recovery: The recovery period is longer, usually around 4-6 weeks.
- Indications: Used for larger cysts, those that are suspected to be cancerous, or when a more comprehensive examination of the abdominal cavity is required.
Why Choose Kalosa Gynae?
- Expertise: Dr. Deepti Asthana is a renowned gynaecologist with extensive experience in treating ovarian cysts.
- Personalised Care: We tailor our treatment plans to meet the unique needs of each patient.
- Advanced Technology: Our clinic is equipped with state-of-the-art technology for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
- Compassionate Support: We provide compassionate care and support throughout your treatment journey.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What causes ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts can be caused by hormonal imbalances, endometriosis, pregnancy, or severe pelvic infections.
Can ovarian cysts affect fertility?
Most ovarian cysts do not affect fertility. However, certain types, such as endometriomas, can impact fertility and may require treatment.
How can I prevent ovarian cysts?
Preventive measures include maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and using hormonal contraceptives if recommended by your doctor.
When should I see a doctor for an ovarian cyst?
You should see a doctor if you experience severe pelvic pain, irregular menstrual cycles, or symptoms of a ruptured cyst, such as sudden sharp pain, fever, or vomiting.
What is the recovery time after ovarian cyst surgery?
Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery. Laparoscopic surgery typically has a shorter recovery period (1-2 weeks) compared to laparotomy (4-6 weeks).